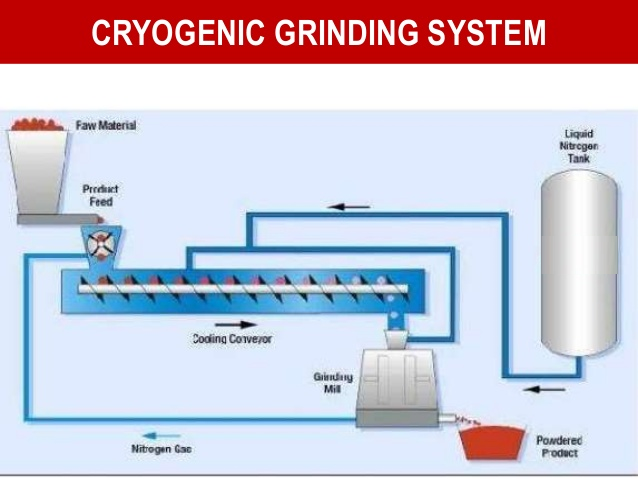
Modified Atmosphere Packaging :: MAP_Process
Everyone knows that food does not stay fresh forever. Milk turns sour, bread goes mouldy, meat develops a brown color and an ‘off’ smell. A number of factors cause food spoilage. Oxygen in the air can cause a process of decay called oxidation. For example fats and oils in food can oxidize to make the food turn rancid.
One of the main causes of the spoilage of food is the growth of microbes such as bacteria, yeasts and mould that are present all around us, even in and on our own bodies. These microbes feed and grow on the food product, causing it to go bad. The appearance of food can also change over time when exposed to air. Fresh meat turns brown after a while because of interactions between oxygen and pigments in the tissue. There are a number of ways to slow down these processes of spoilage and to keep food attractive and edible for as long as possible.
These include simple refrigeration – the lower the temperature the slower most microbes will grow – or treatments such as pickling, curing with salt or by adding artificial preservatives. However, to keep food fresh for as long as possible without additives is a challenge, and one key technology for achieving this goal is to seal the food product in a package which contains a mixture of natural gases in carefully controlled proportions that significantly slow down the process of decay by inhibiting processes of oxidation and the growth of microbes.
This is the essence of modified atmosphere packaging: the atmosphere in which the food is packaged is modified so that spoilage is markedly reduced and the shelf life of the product is increased.The type and proportion of gas used in the packaging is largely dictated by the type of food in the package and the sort of decay or change that the food undergoes.To package a product in a modified atmosphere requires sophisticated machinery to flush out air from the packaging chamber and replace it with a different gas or precisely defined mixture of gases, then seal the product in the packaging so that only the modified atmosphere surrounds the product and not any other unwanted gas.


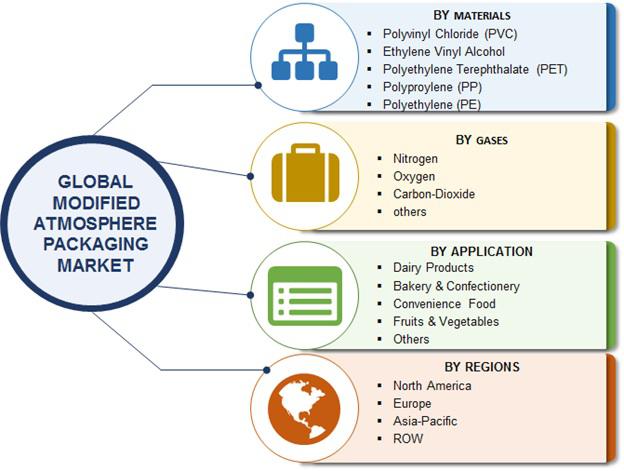

Cryogenic Grinding System
The extremely low temperature are produced by using substances called ‘cryogenic 'such as LIQUID NITROGEN and LIQUID HELIUM.
Cryogenic grinding , also known as freezer milling/freezer grinding/ cryo milling is the act of cooling or chilling a material and then reducing it to smaller particle size.
Almost all materials em brittle when exposed to low temperature. Cryogenic size reduction utilizes the cooling effect of liquid nitrogen to em brittle materials prior to and or during the grinding process.
Materials which are elastic in nature, which have low melting points, which have low combustion temperatures and which are sensitive to oxygen can be ideally machined by cryogenic grinding process.
Advantages of cryogenic grinding
Higher material removal rate can be achieved.
Tool wear and tear is minimized to a great extent.
Grinding forces are reduced.
Cryogenics act as coolant and hence the effects of overheating of the tool and work piece are reduced.
Materials which are soft and elastic in nature such as rubber can be easily machined with this process.
Smaller particle size can be achieved.
Better surface finish and dimensional accuracy can be achieved.