Power and Energy
Power is the rate of doing work, the amount of energy transferred per unit time. ... In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the joule per second (J/s)
Wind power
Wind power is the use of air flow through wind turbines to mechanically power generators for electricity. Wind power, as an alternative to burning fossil fuels, is plentiful, renewable, widely distributed, clean, produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, consumes no water, and uses little land.The net effects on the environment are far less problematic than those of nonrenewable power sources.
Wind farms consist of many individual wind turbines, which are connected to the electric power transmission network. Onshore wind is an inexpensive source of electric power, competitive with or in many places cheaper than coal or gas plants. Offshore wind is steadier and stronger than on land and offshore farms have less visual impact, but construction and maintenance costs are considerably higher. Small onshore wind farms can feed some energy into the grid or provide electric power to isolated off-grid locations.
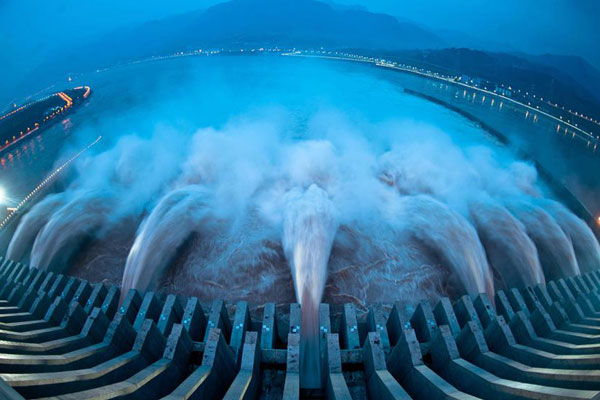
Hydro Electricity
Hydro Electricity is generated by harnessing the power of moving water. It is manufactured in large power generating stations using the same basic principle of a small grist mill yet on a much larger and vastly improved scale for better efficiency. Electrical generators are attached to huge turbine devices which spin at great speeds as a result of water rushing through them.
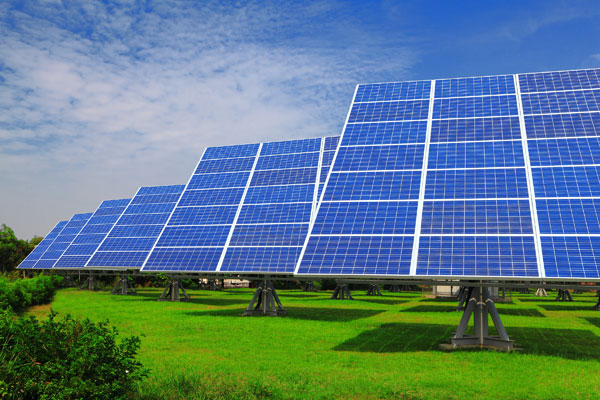
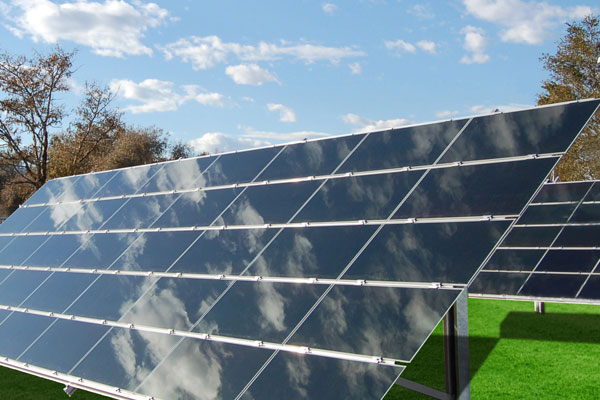
Solar Electricity
Solar Electricity is generated with the only power that has been in existence since the living breathed on this planet, the huge and singular source named as Sun. The sun rays are the only source in Solar Electricity. It is generated with the help of Photovoltaic (PV) technology by converting solar energy into solar electricity from sunlight. PV Systems use sunlight to power ordinary electrical equipments for example: household appliances, computers & lightings.